What is Down Syndrome?
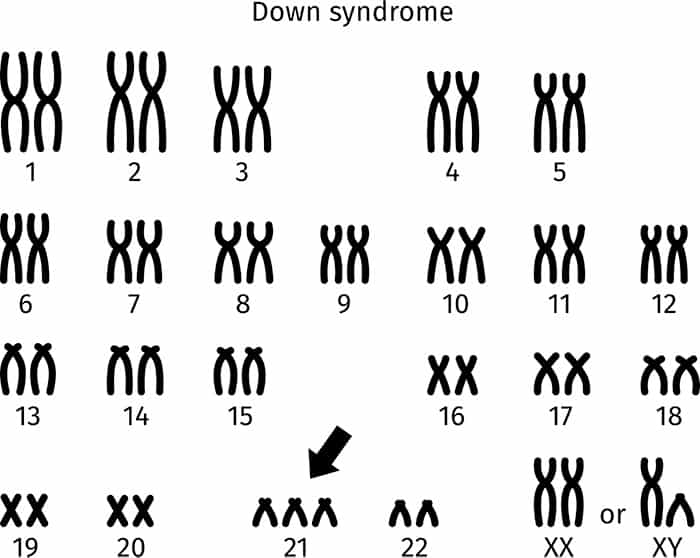
Down syndrome occurs when an individual has a full or partial extra copy of chromosome 21.
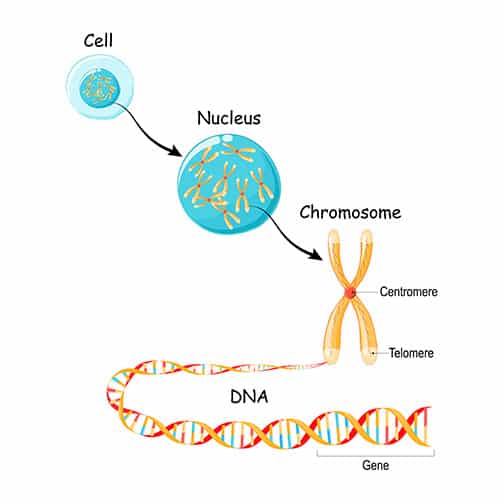
In every cell in the human body there is a nucleus where genetic material is stored in genes. Genes carry the codes responsible for all of our inherited traits and are grouped along rod-like structures called chromosomes. Typically, the nucleus of each cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 chromosomes total), half of which are inherited from each parent. Down syndrome occurs when an individual has a full or partial extra copy of chromosome 21.
This additional genetic material alters the course of development and causes a variety of common traits associated with Down syndrome. Each person with Down syndrome is a unique individual and may possess some of these characteristics to different degrees, or not at all. Some common features include low muscle tone or loose joints, smaller stature, small hands and feet, an upward slant to the eyes, a protruding or larger tongue, a single deep crease across the center of the palm (palmar crease), and mild to moderate cognitive delays.
For centuries, people with Down syndrome have been alluded to in art, literature and science. It wasn’t until the late nineteenth century, however, that John Langdon Down, an English physician, published an accurate description of a person with Down syndrome. It was this scholarly work, published in 1866, that earned Down the recognition as the “father” of the syndrome. Although other people had previously recognized the characteristics of the syndrome, it was Down who described the condition as a distinct and separate entity.

John Langdon Down
In recent history, advances in medicine and science have enabled researchers to investigate the characteristics of people with Down syndrome. In 1959, the French physician Jérôme Lejeune identified Down syndrome as a chromosomal condition. Instead of the usual 46 chromosomes present in each cell, Lejeune observed 47 in the cells of individuals with Down syndrome. It was later determined that an extra partial or whole copy of chromosome 21 results in the characteristics associated with Down syndrome. In the year 2000, an international team of scientists successfully identified and cataloged each of the approximately 329 genes on chromosome 21. This accomplishment opened the door to great advances in Down syndrome research.

Jérôme Lejeune
There are three types of Down syndrome: Trisomy 21 (Nondisjunction), Translocation, and Mosaicism.
Typical Cell Division:

Trisomy 21 (Nondisjunction)
Down syndrome is usually caused by an error in cell division called “nondisjunction.” Nondisjunction results in an embryo with three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the usual two. Prior to or at conception, a pair of 21st chromosomes in either the sperm or the egg fails to separate. As the embryo develops, the extra chromosome is replicated in every cell of the body. This type of Down syndrome, which accounts for 95% of cases, is called trisomy 21.
Cell division in Trisomy 21:

Mosaicism
Mosaicism (or mosaic Down syndrome) is diagnosed when there is a mixture of two types of cells, some containing the usual 46 chromosomes and some containing 47. Those cells with 47 chromosomes contain an extra chromosome 21.
Mosaicism is the least common form of Down syndrome and accounts for only about 1% of all cases of Down syndrome. Research has indicated that individuals with mosaic Down syndrome may have fewer characteristics of Down syndrome than those with other types of Down syndrome. However, broad generalizations are not possible due to the wide range of abilities people with Down syndrome possess.
Cell division in Mosaicism:

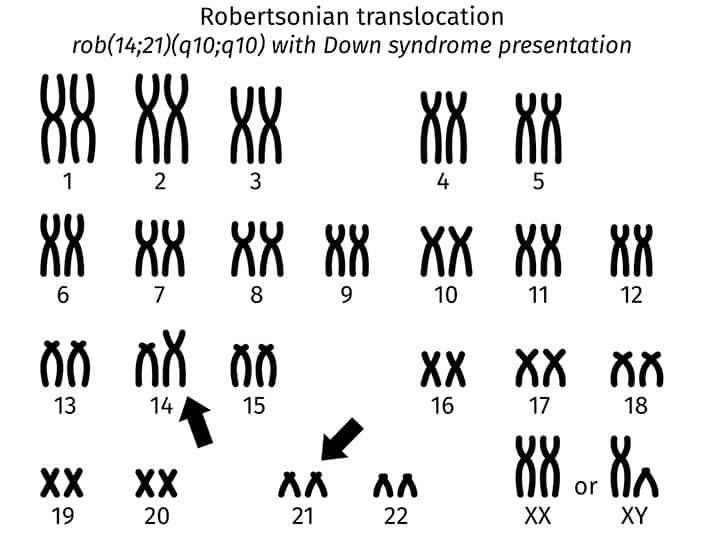
Translocation
In translocation, which accounts for about 4% of cases of Down syndrome, the total number of chromosomes in the cells remains 46; however, an additional full or partial copy of chromosome 21 attaches to another chromosome, usually chromosome 14. The presence of the extra full or partial chromosome 21 causes the characteristics of Down syndrome.
Regardless of the type of Down syndrome a person may have, all people with Down syndrome have an extra, critical portion of chromosome 21 present in all or some of their cells.
The cause of the extra full or partial chromosome is still unknown and can originate from either the father or the mother. Maternal age is the only factor that has been linked to an increased chance of having a baby with Down syndrome resulting from nondisjunction or mosaicism. However, due to higher birth rates in younger women, 80% of children with Down syndrome are born to women under 35 years of age.
There is no definitive scientific research that indicates that Down syndrome is caused by environmental factors or the parents’ activities before or during pregnancy.
All 3 types of Down syndrome are genetic conditions (relating to the genes), but only 1% of all cases of Down syndrome have a hereditary component (passed from parent to child through the genes). Heredity is not a factor in trisomy 21 (nondisjunction) and mosaicism. However, in one-third of cases of Down syndrome resulting from translocation there is a hereditary component – accounting for about 1% of all cases of Down syndrome.
The age of the mother does not seem to be linked to the risk of translocation. Most cases are sporadic – chance – events. However, in about one-third of cases, one parent is a carrier of a translocated chromosome.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately one in every 700 babies in the United States is born with Down syndrome, making Down syndrome the most common chromosomal condition diagnosed in the United States.
Down syndrome occurs in people of all races and economic levels, though older women have an increased chance of having a child with Down syndrome. A 35-year-old woman has about a one in 365 chance of conceiving a child with Down syndrome, and this chance increases gradually to 1 in 100 by age 40. At age 45 the incidence becomes approximately 1 in 30.
Once a woman has given birth to a baby with trisomy 21 (nondisjunction) or translocation, it is estimated that her chances of having another baby with trisomy 21 is 1 in 100 up until age 40.
The risk of recurrence of translocation is about 3% if the father is the carrier and 10-15% if the mother is the carrier. Genetic counseling can determine the origin of translocation.
Prenatally
There are two categories of tests for Down syndrome that can be performed before a baby is born: screening tests and diagnostic tests. Prenatal screens estimate the chance of the fetus having Down syndrome. These tests do not tell you for sure whether your fetus has Down syndrome; they only provide a probability. Diagnostic tests, on the other hand, can provide a definitive diagnosis with almost 100% accuracy.
There is an extensive menu of prenatal screening tests now available for pregnant women. Most screening tests involve a blood test and an ultrasound (sonogram). The blood tests (or serum screening tests) measure quantities of various substances in the blood of the mother. Together with a woman’s age, these are used to estimate her chance of having a child with Down syndrome. These blood tests are often performed in conjunction with a detailed sonogram to check for “markers” (characteristics that some researchers feel may have a significant association with Down syndrome). New advanced prenatal screens are now able to detect chromosomal material from the fetus that is circulating in the maternal blood. These tests are not invasive (like the diagnostic tests below), but they provide a high accuracy rate. Still, all of these screens will not definitively diagnose Down syndrome. Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests are now routinely offered to women of all ages.
The diagnostic procedures available for prenatal diagnosis of Down syndrome are chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis. These procedures, which carry up to a 1% risk of causing a spontaneous termination (miscarriage), are nearly 100% accurate in diagnosing Down syndrome. Amniocentesis is usually performed in the second trimester between 15 and 20 weeks of gestation, CVS in the first trimester between 9 and 14 weeks.
At Birth
Down syndrome is usually identified at birth by the presence of certain physical traits: low muscle tone, a single deep crease across the palm of the hand, a slightly flattened facial profile and an upward slant to the eyes. Because these features may be present in babies without Down syndrome, a chromosomal analysis called a karyotype is done to confirm the diagnosis. To obtain a karyotype, doctors draw a blood sample to examine the baby’s cells. They photograph the chromosomes and then group them by size, number, and shape. By examining the karyotype, doctors can diagnose Down syndrome. Another genetic test called FISH can apply similar principles and confirm a diagnosis in a shorter amount of time.
Each and every person with Down syndrome is unique and valuable to their families and to society.
Babies born with Down syndrome will grow and develop like all other babies, but typically at a slower pace. Children with Down syndrome may be delayed in achieving milestones compared to neurotypical children.
Individuals with Down syndrome possess varying degrees of cognitive delays, but the effect is usually mild to moderate. Despite this, those with Down syndrome have many strengths, talents, and abilities that make them unique.
There is an increased risk for certain medical conditions in individuals with Down syndrome such as congenital heart defects, gastrointestinal issues, respiratory and hearing problems, Alzheimer's disease, childhood leukemia, and thyroid conditions. Most of these conditions are treatable, and people with Down syndrome lead long, healthy lives. In fact, life expectancy for people with Down syndrome has increased dramatically from 25 in 1983 to 60 and older today.
The future of those with Down syndrome is bright! Quality educational programs are available, and some are continuing on to post-secondary education opportunities, as well. Many individuals with Down syndrome love to work and volunteer, as well as participate in a variety of recreational and community activities. They live independently, in supported living communities, in group settings, or with their parents. With positive support from family, friends, and the community, people with Down syndrome are able to develop their full potential and lead exciting and fulfilling lives!
The Down Syndrome Association of South Texas offers a variety of programs for people with Down syndrome of all ages and their family members.
Please contact us at [email protected] or 210.349.4372 with any questions you may have.
Some of the programs we offer are...
New and Expectant Parent Support
Grupo de Apoyo en Español for Spanish-speaking families
...and a variety of social programs for different ages. These programs are a great opportunity to meet new families and develop friendships that will last a lifetime!
The DSASTX also offers monthly educational programs for parents, guardians, and community professionals.
For more information on our programs and events, please visit each program page or the Calendar of Events.
